Introduction
Adding and verifying a sending domain inside your Resend account is mandatory before you can start relaying messages through the Gravity SMTP Resend Integration.
See Resend’s documentation on Creating a sending domain guide.
Adding a New Domain
From your Resend dashboard.
- Go to Domains.
- Click Add Domain.
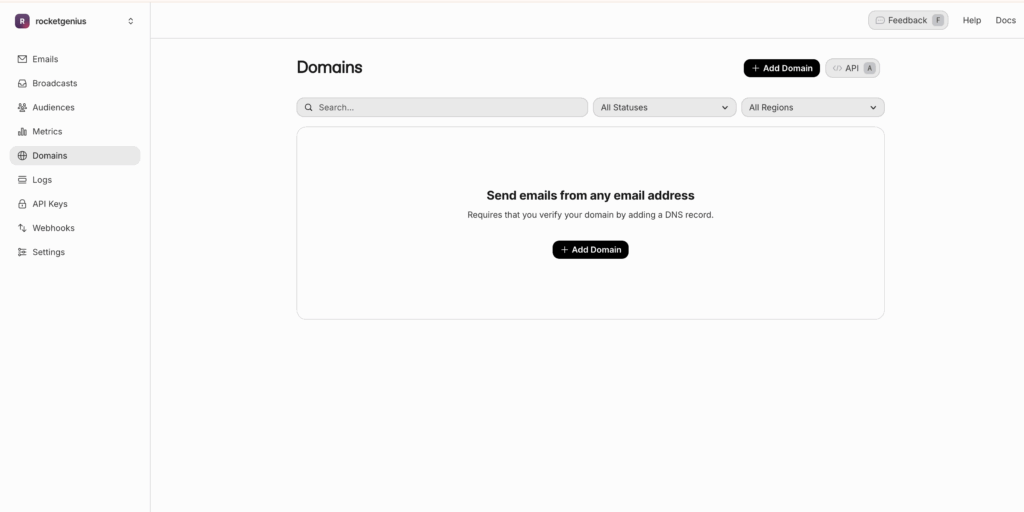
- Enter the domain (or sub-domain) you plan to send from and click Add Domain.
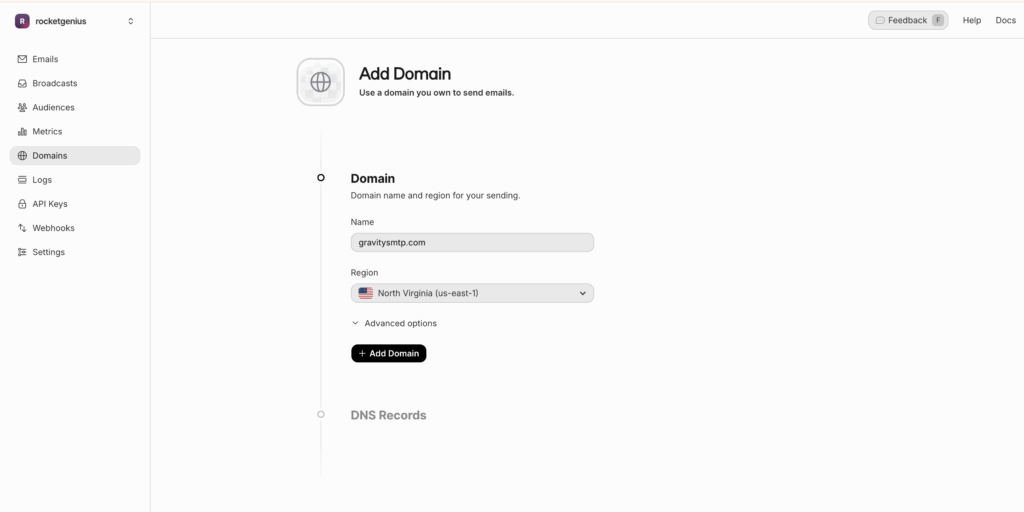
- Once added, Resend will show the required configuration for your DNS service.
Adding DNS Records
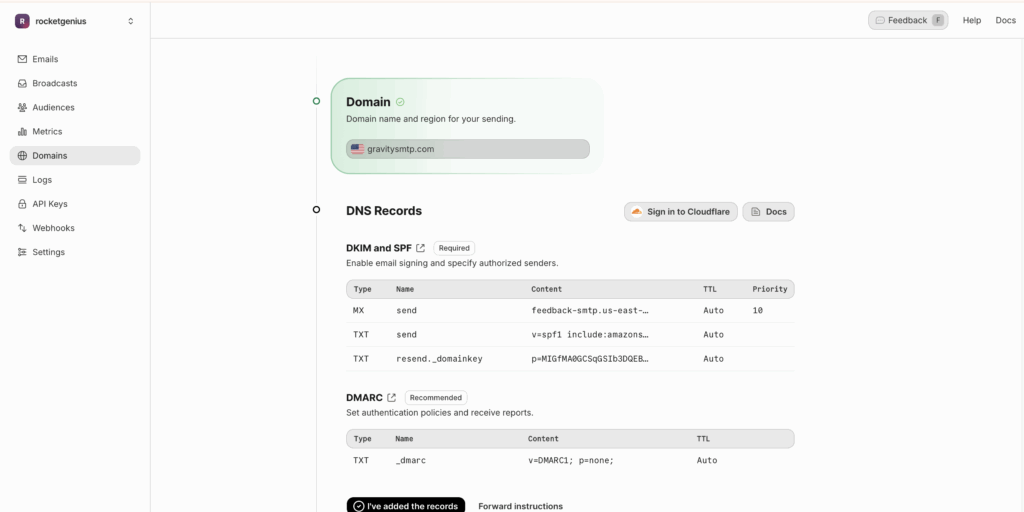
Resend generates the DNS records you need. Once you click on the domain, the records will appear in the domain’s detail pane.
MX (Mail Exchange) records for receiving designate the mail server responsible for accepting email messages on behalf of a domain. They direct sending mail servers on where to route emails for a specific domain, ensuring that messages are delivered to the correct destination.
SPF (Sender Policy Framework) records for sending exist as a TXT record and are designed to prevent email spoofing. They specify which mail servers are permitted to send email on behalf of your domain, improving email delivery accuracy and preventing your domain from being used for phishing or spam.
DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) records for sending exist as a TXT record and are used to authenticate emails, confirming messages are actually from the domain they claim to be from and have not been tampered with during transmission. This enhances email security, mitigates the risk of email spoofing, and increases the likelihood of legitimate emails reaching their intended recipients.
Add the records at your DNS host exactly as shown in Resend. All records live on a subdomain of the sending domain (e.g. resend.mail.example.com).
Verifying Domain Ownership
After publishing the records.
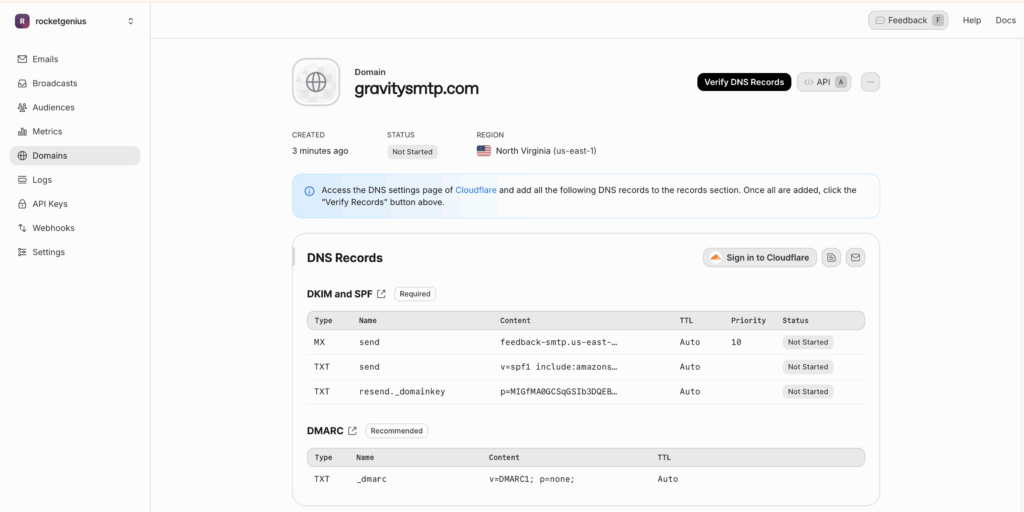
- Return to Domains.
- Click Check DNS next to your domain. Resend will query each record and update the status indicators.
- Propagation can take up to 24 hours. While you wait, you’ll see warnings such as SPF or DKIM missing; these disappear once the records resolve.
When all checks pass, the domain status changes to Verified.